Gov't to Shift Industrial
Structure to Advanced,
Innovative One
i-Manufacturing aimed at upgrading Korea's core
manufacturing industries with a view of becoming
a global top four powerhouse
 The government has come up with a Korean version of i-Manufacturing, designed to upgrade Korea's core manufacturing industries to the world's top-notch standards with the goal of raising the per capital national income to $35,000 and developing the country into the global top four industrial powerhouse by 2015.
The government has come up with a Korean version of i-Manufacturing, designed to upgrade Korea's core manufacturing industries to the world's top-notch standards with the goal of raising the per capital national income to $35,000 and developing the country into the global top four industrial powerhouse by 2015.
The i-Manufacturing scheme calls for raising the combined annual sales of Corporate Korea from an average of 620 trillion during the period between 1999 and 2004 to 2,700 trillion won as it strives to strengthen the conventional manufacturing sector's capability by capitalizing on its strong IT foundation.
Park In-gyu, deputy director of Industrial Machinery & Aerospace Industries Division at the Ministry of Commerce, Industry and Energy (MOCIE), said, "The Korean-type i-Manufacturing scheme is aimed at shifting Korea's industrial structure into an innovative one based on such invisible assets as knowledge, technology and information as key growth engines in a bid to cope with such problems as worsened industrial bi-polarization between rich large-size companies and poor small-size ones and a lack of key source technologies in some sectors."A shift in industrial structure is badly needed at a time when Korea is striving to secure an international edge to cope with such rapid changes in the global manufacturing environment as the proposed FTA deal with Japan, a chase by developing countries, including China, and competition with advanced nations, he said.
Amid this changing manufacturing background, the MOCIE launched a pilot program designed to build up infrastructure for e-Manufacturing as part of its efforts to promote collaboration and technological development among companies in 2004. The e-Manufacturing project is referred to a scheme designed to promote informatization of the manufacturing sector by innovating and integrating new product development, procurement, production, logistics, after-sales and other manufacturing processes, management/transaction and transaction methods, based on Korea's strong IT infrastructure.
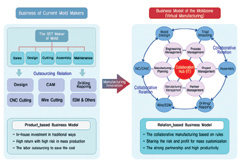
Sixty-one large and small-sized companies are participating under collaboration hub projects involving in four areas, including molding design, molding production, which is organized by the Korea Institute of Industrial Technology (KITECH).
A case in point is the Mold Zone Collaboration Program comprising of nine molding companies in Siheung City. The member companies, independent entities, work together under a collaboration program for each project, so the strong point of the Mold Zone Collaboration Program is for each company to concentrate its energy on its assigned task. The Mold Zone has made media headlines with its tremendous feat ¡ª a six-fold surge in sales in two years.
Director Park quoted MOCIE Minister Chung Sye-kyun as saying that e-Manufacturing will become ways of solving the snowballing disparity between large- and small-size enterprises, an issue the minister pledged to tackle during his recent inauguration ceremony.
The United States has implemented a top-down manufacturing system in which large-size corporations develop and disseminate such innovation methods as SCM, PLM and Six-Sigma programs to their subcontractors. In Japan, SMEs have adopted "bottom-up quality innovation programs"by making the most of traditional craftsmanship and collaborative ties between small and large-size companies.
On the other hand, Park said, the MOCIE is striving to implement a Korean "Middle-Updown"version of i-Manufacturing in which midsize companies pursue horizontal collaboration to step up their competitive edge while disseminating innovative technologies with smaller firms and strengthen collaborative ties with large corporations.
E-Manufacturing is one of the six core tasks being implemented under the Korean version of i-Manufacturing scheme. The other five tasks is about the establishment and operation of a new product development support center; development of manufacturing equipment and system for reconfigurability; building up infrastructure for creating horizontal collaboration network, development of environmentally-friendly and human-oriented manufacturing technologies; and cultivation of manpower specializing in manufacturing innovations. nw
3Fl, 292-47, Shindang 6-dong, Chung-gu, Seoul, Korea 100-456
Tel : 82-2-2235-6114 / Fax : 82-2-2235-0799